Photographs to recognize the hand-foot-mouth virus in babies
One of the most proliferating viruses in day care centers is the so-called hand-foot-mouth virus . And although at first it is more typical of preschool children, it can also affect older children. Even in adults. But ... would you recognize it? How to differentiate it from similar diseases such as
One of the most proliferating viruses in day care centers is the so-called hand-foot-mouth virus. And although at first it is more typical of preschool children, it can also affect older children. Even in adults. But ... would you recognize it? How to differentiate it from similar diseases such as chicken pox? Photographs showing how hand-foot-mouth disease is in children
(Photographs from the Wikimedia Commons)
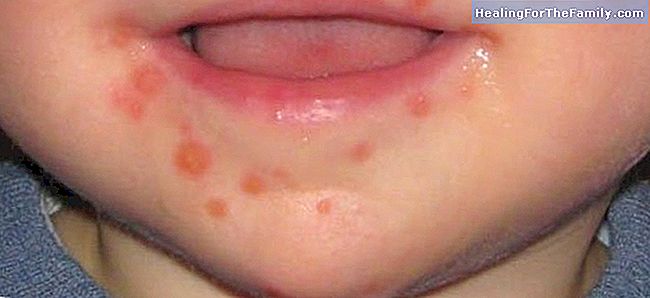
Undoubtedly, hand-foot-mouth disease is
very common among children under 5 years old . And tremendously contagious. Therefore, at the first symptom, pediatricians recommend that parents not take their child to daycare or school. In fact, such is the expansion of this virus, that experts insist on spreading photographs that help parents recognize it.The disease, called in the medical field as
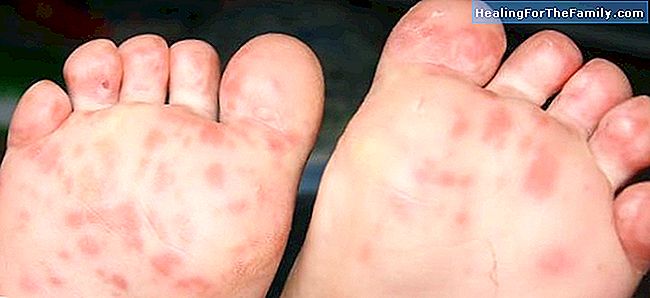
Coxsackie disease, is transmitted by a virus, which means that it first incubates until the first signs appear: small ulcers and rashes around the mouth, hands and feet. To catch it, a kiss or a sneeze is enough ... The hand-foot-mouth virus
usually starts attacking the throat. The child complains of a strong sore throat. However, these symptoms may suggest that it is angina or pharyngitis. The next symptom is fever. Soon after, the appearance of small ulcers, the most conclusive data to diagnose the virus. Like any other virus, there is no drug treatment.
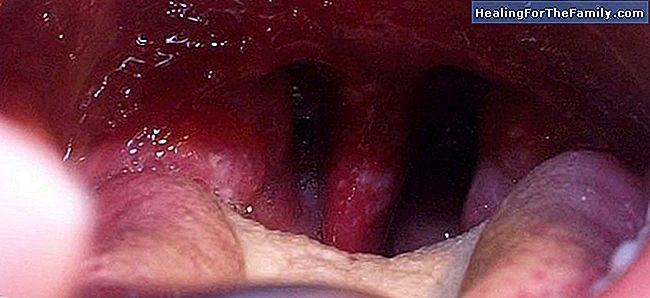
Only acetaminophen or ibuprofen (never aspirin). It is important to insist that the child drink a lot and take cold foods (which calms the pain of the ulcers), since babies with this disease tend to stop eating and drinking, because of the sore throat and the ulcers around the mouth. The greatest danger, therefore, is that of dehydration. The disease, although at first it seems alarming, is not dangerous. After three days, the fever tends to disappear, although the rest of the symptoms do not disappear until 7-10 days. Of course, to avoid contagion to fillies people (including parents), experts recommend extreme hygiene:
- Wash your hands very well - Do not kiss the baby affected by the disease- Change the diaper with disposable gloves
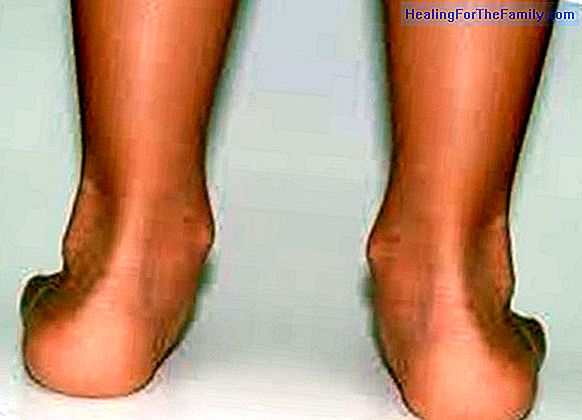
A of the consequences of this disease is
the loss of some nail of the feet.
And in extreme cases (they occur very rarely), it can lead to encephalitis.