Common childhood diseases caused by viruses
Infections and diseases can usually be caused by viruses or bacteria. Many times we refer to them as if they were the same thing, however they have great differences and cause different diseases. Viruses are organisms that do not have cells but do have their own metabolism . To reproduce they need t
Infections and diseases can usually be caused by viruses or bacteria. Many times we refer to them as if they were the same thing, however they have great differences and cause different diseases.
Viruses are organisms that do not have cells but do have their own metabolism. To reproduce they need to occupy the cells of another living organism. They do not move or grow but they mutate and reproduce.
Common childhood diseases caused by viruses

Infections caused by viruses are more difficult to treat since these microorganisms live inside the cells of the body, in this way, they are protected against medicines, in fact, antibiotics do not work against them. Vaccines are our great allies against them. In Guiainfantil.com we tell you what are the common diseases caused by viruses.
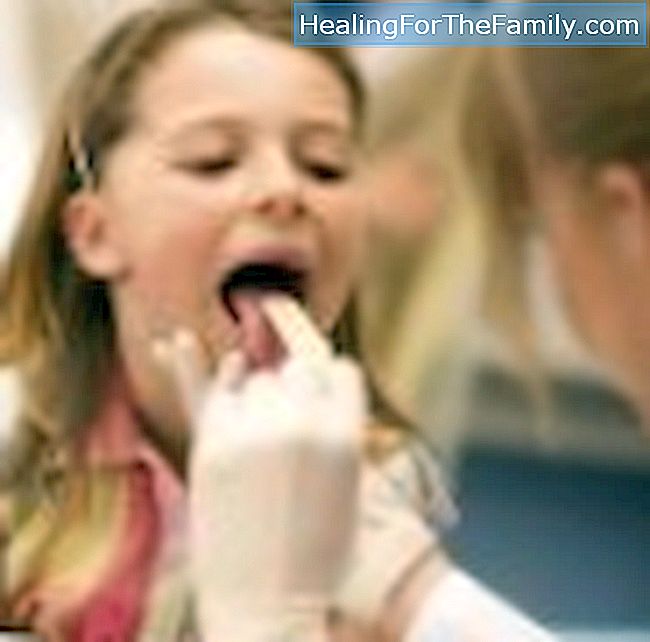

Mononucleosis. What is mononucleosis? Many know it as the kissing disease since mononucleosis is transmitted by saliva. We tell you what are the symptoms, causes, diagnosis and treatment of mononucleosis. It causes fever, sore throat and malaise, but it is easy to treat.

Catarrh Children and babies with catarrh, a condition caused by a virus. Its symptoms and treatment in childhood. Common diseases in children and babies.
Measles. Measles in children and babies who were not vaccinated. Measles is an infectious-contagious disease that affects unvaccinated small children.

Flu. Seasonal flu is a viral infection of the upper part of the respiratory system and this virus is transmitted through the air, through the cough or sneezing of infected persons, or through direct contact through the skin rubbing. For this reason, it is very important to wash your hands frequently and avoid wearing them on your face.

Herpes. What is infantile herpes? Child herpes is a frequent viral infection, which occurs in two varieties: cold sores or type I and herpes zoster or type II. Causes and cure of infantile herpes in children. Symptoms of childhood herpes.

Parioditis or mumps. Papera is a highly contagious disease in children although it is not a worrisome or serious pathology, so parents should not be alarmed by the parioditis.

Cold. Cold viruses are quickly spread between children and babies, since they are easily transmitted by contact and orally. In addition, they take advantage of the cooling of mucous membranes when it is cold to enter the body. Everything you can do to prevent children from catching a cold.

Rubella. What is the cause and cure of rubella in children? Symptoms of the disease in children and babies. Most common childhood diseases, their symptoms and treatment.

Varicella. Chickenpox is an infectious disease that is characterized by fever and the appearance of rashes on the skin of a child and babies. Most common childhood diseases in children and babies.

Poliomyelitis. The polio virus multiplies in the central nervous system and causes severe paralysis. Vaccine against poliomyelitis. Most common child diseases.

Hepatitis B. What is hepatitis B and how is it transmitted? Guiainfantil offers all the information about hepatitis B in childhood. Symptoms, infection, diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis B in children and babies.

Hepatitis A. Hepatitis A in children. What symptoms does hepatitis A have and how is it diagnosed in children? Guiainfantil.com offers all the information about the treatment of hepatitis A in children.

Human papilloma virus. The Human Papilloma Virus comprises a group of 100 different viruses that cause skin lesions and many are responsible for the most frequent sexually transmitted infections in the world.

Viral exanthema. Viral exanthema in children is a mild disease caused by a type of human herpes virus that causes fever and rashes similar to those of measles and rubella.