How epidural anesthesia is applied at delivery
The application of epidural anesthesia in labor usually takes a few minutes. It is a technique that in principle is not complicated, but it is something delicate and must be administered by an anesthetist . Epidural anesthesia has its advantages and disadvantages and its application is a very person
The application of epidural anesthesia in labor usually takes a few minutes. It is a technique that in principle is not complicated, but it is something delicate and must be administered by an anesthetist.
Epidural anesthesia has its advantages and disadvantages and its application is a very personal decision of the pregnant woman. It is a very common technique nowadays, although it has some risks that are also important to know. Knowing, in any case, how it is administered and what will happen, step by step, will help the pregnant woman to live this moment more calmly.
How and when epidural anesthesia is applied
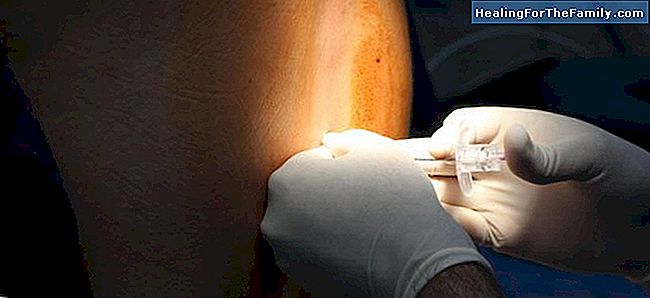
Before the puncture:
- The nurse or midwife will take you a peripheral route through which you will put at least 500 ml of saline to prevent hypotension.
- Blood pressure is taken.
- Vaginal touch is performed, to know when we are in labor.
During the puncture:
- The woman will be taught what position she should have at all times (the most important thing is that the woman does not move at all); usually sitting like a tailor, and with his back arched like an angry cat (or a shrimp, some say). The goal of the posture is to open the intervertebral space. Some anesthetists prefer that the woman lie on her side, placing her back in the same way as the one just explained.
- At all times the woman and the baby have controlled vital signs.
- Sterilization. Clean the area on your back using a sterilizing solution.
- Local anesthesia is applied so that it will not hurt when you have an epidural. The needle used in this step can cause a mild and temporary sensation, like any other injection in your skin. It usually feels stinging when local anesthesia is infiltrated. A - From this point it is very important to stay still
, the most likely thing is that the anesthetist or the midwife who is with you will explain what is going to happen, so that you do not take anything by surprise. - Puncture: the anesthetistwill place a thick needle in the epidural space
, which is a layer of tissue, fluid and fat inside your spine, between the dura and the vertebra, which protects the spinal cord. Because the area of the skin is under the effects of local anesthesia, it does not really hurt when you have the epidural; nothing else you feel the pressure of the doctor to introduce the needle. - Placement of the catheter: frequentlya catheter is left inserted in the area,
to leave an anesthesia perfusion throughout the delivery. - The midwife fixes it with tape to the skin. You can support your back, but try not to drag it when you turn, to prevent the plaster from peeling off and the catheter moving. -
The effect of epidural anesthesia begins to be felt 10 to 20 minutes after its application
. Depending on the intensity and duration of your labor, you may require additional doses of the medication.












