Children's intolerance to fructose
Hereditary fructose intolerance (IHF) in children is a disease caused by the absence of an enzyme that transforms the sugar contained in fruit and honey. This genetic alteration prevents fructose from being synthesized in the proper way for the child's organism, accumulating in the liver, kidneys or
Hereditary fructose intolerance (IHF) in children is a disease caused by the absence of an enzyme that transforms the sugar contained in fruit and honey.
This genetic alteration prevents fructose from being synthesized in the proper way for the child's organism, accumulating in the liver, kidneys or intestine.
What is the fructose intolerance

Fructose or levulose is the type of sugar that both fruit and honey contain. While the table sugar is formed from the union of glucose and fructose, the fructose itself in a monosaccharide formed by a single link.
This means that it does not need to be digested and can pass directly into the bloodstream from the intestine, to complete its process in the liver, where it is transformed into fructose 1 phosphate, a new substance on which the enzyme aldolase B acts, responsible for the transformation of fructose to produce, for example, energy.
Symptoms and treatment of fructose intolerance in children
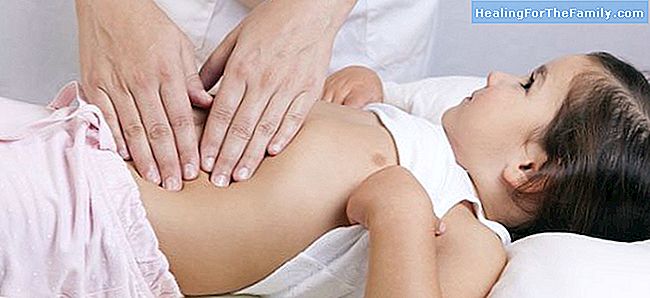
The first symptoms that appear when a child is fructose intolerant, after the consumption of a food with this type of sugar, are abdominal pain and vomiting that may lead to severe hypoglycaemia
The treatment is basically preventive. The child's diet must be controlled to avoid the intake of fruit or honey. In addition, other types of sugars, such as sucrose or sorbitol, should be avoided.
But by eradicating the fruit from the child's diet, the largest source of vitamin C, necessary for the proper development of children, is also being eliminated, so it is recommended to supplement the absence of this nutrient.
Difference between fructose intolerance (IHF) and malabsorption of fructose
Fructose malabsorption is a more common disease than hereditary fructose intolerance, and occurs approximately in 30% of the population world. In this case, intestinal cells are not able to completely absorb fructose, causing abdominal pain, gas, diarrhea or nausea in the child.
Diego Fernández. Editor of Guiainfantil.com