Tympanic perforation in children
With the beginning of the school year, respiratory infections become more frequent. One of the complications most feared by parents is otitis media, due to the discomfort it produces. In some cases, the accumulation of mucus and pus in the middle ear causes the eardrum to bulge so much that it ends
With the beginning of the school year, respiratory infections become more frequent. One of the complications most feared by parents is otitis media, due to the discomfort it produces. In some cases, the accumulation of mucus and pus in the middle ear causes the eardrum to bulge so much that it ends up breaking. Imagine a balloon. If we inflate it, at the beginning it will be able to relax without problems. But if we continue to inflate it more and more, the tension inside it ends up generating a perforation and the gaseous content will come out suddenly: the same happens in some otitis, with mucopurulent content stored. In this case, we are faced with a case of perforated eardrum in children.
Causes of perforation of the eardrum in children
The most frequent cause is infectious (otitis), but there is more: accidental introduction of a pointed foreign body, strong trauma to the ear (for example: a slap), use of swabs, exposure to a high intensity noise, rapid change of pressure (diving), etc.
Symptoms of tympanic perforation in childhood
It might seem that the perforation of the eardrum hurts. Well, the opposite happens. Otitis media hurts a lot, precisely until the eardrum breaks. In the pre-perforation phase, the child is irritable, cries incessantly and tends to cover his ear with his hand.
When the perforation occurs, the minor is more relieved, and we will be able to appreciate the exudation through the external ear of mucus, pus and -as in any wound- blood. In a generally transient way, the child will lose hearing acuity and may hear a ringing / buzzing sound. Also, you may feel dizzy
Diagnosis of ruptured eardrum in children
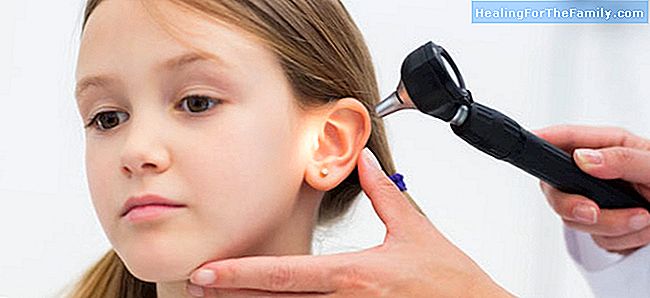
By the clinic. In addition, with the help of the otoscope, the doctor will be able to determine the location of the open hole in the eardrum, as well as the discharge of secretions through it.
Treatment for a perforated eardrum in children
Suppurated otitis is treated with a broad-spectrum antibiotic administered orally, for 10 days. The first choice is amoxicillin. In addition, we can resort to general measures (oral ibuprofen and dry local heat for pain). An
earplug should be placed only when we go to clean the child , so that water does not enter the middle ear. We have to clean only the secretions externalized to the auditory pavilion with the tip of a towel, a gauze or cotton, avoiding the introduction of sticks.The normal evolution of this type of process is towards complete healing. In a few days, the eardrum regains its integrity, through a small scar shaped "fly wing". Only in a small percentage of cases, the perforation does not close properly spontaneously. In them, specific assessment by an otorhinolaryngologist is required.