What is amniocentesis for in pregnancy
During pregnancy, the woman undergoes many tests, tests, analyzes with the objective of evaluating the wellbeing of the mother and the baby, and of course, assessing that the pregnancy takes place without no complication One of the tests that many women are subjected to when labor begins is amniosco
During pregnancy, the woman undergoes many tests, tests, analyzes with the objective of evaluating the wellbeing of the mother and the baby, and of course, assessing that the pregnancy takes place without no complication
One of the tests that many women are subjected to when labor begins is amnioscopy, a controversial technique according to different scientific studies.
What and how amnioscopy is performed on the pregnant woman
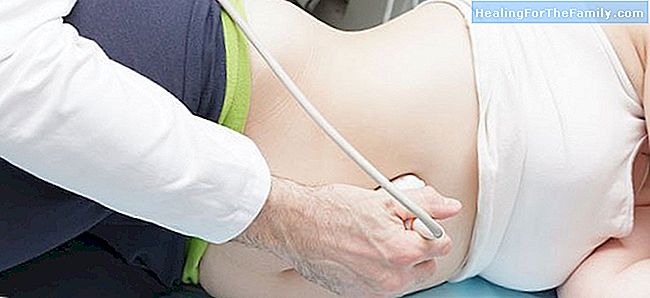
Amnioscopy is an invasive test and consists in introducing a hollow tube through the cervix, through which we introduce a cold light, and observe through the vagina the amniotic fluid. To perform this test it is necessary that the cervix is dilated one or two centimeters. This dilation can be obtained manually before the test.
The purpose of the test is to detect the presence of meconium in the amniotic fluid. Meconium is a dark, viscous substance that forms in the intestine of the fetus and is expelled as first stool.
The presence of meconium in the amniotic fluid is usually associated with problems before delivery, since it is often attributed to the expulsion of feces by the fetus as a result of hypoxia (lack of oxygen), and after delivery the baby could aspirate the meconium into the lungs.
However, it is necessary to explain to the woman that the fetus physiologically performs many of the functions that it will do when it is born, and one of them is to swallow amniotic fluid, digest it and expel it in the form of dark and viscous stools that we call meconium.
The usefulness of amnioscopy is currently questioned, since only allows to assess the presence of meconium in the lower pole and not in the entire of the amniotic fluid pocket. In addition, the presence of meconium, by itself, does not necessarily indicate fetal distress; this suspicion must be confirmed with a cardiotocographic record (the monitors that put us in the hospital)
According to the Clinical Practice Guide for Normal Birth Care, 'amnioscopy is a procedure that is practiced to evaluate the amount and / or color of amniotic fluid (LA) in order to detect alterations that could indicate fetal compromise. However, it is an invasive procedure that is not exempt from complications and with a significant number of false results. These circumstances determine that the benefit-risk balance is doubtful.
Risks of amnioscopy for the baby and the pregnant woman
Amnioscopy has risks: During amnioscopy, the amniotic fluid bag may rupture, or a membrane detachment may occur. The rupture of the bag carries a risk of infection, and the detachment of membranes can cause dilation of the cervix, infections, hemorrhages or accidental rupture of the amniotic sac. It is also a test that is very annoying for women.
Currently, it is not indicated to perform this test routinely, unless we suspect meconium. Even so to check the welfare of the baby, the indicated thing is to carry out a cardiotocographic monitoring, which will give us more data.











