How to differentiate measles, varicella and rubella in children
There are three viral infections that occur with pimples-spots on the skin, and that often cause confusion among the parents of children who suffer them. Measles, chicken pox and rubella are highly contagious viral diseases and, on occasions, difficult to differentiate , especially for parents, sinc
There are three viral infections that occur with pimples-spots on the skin, and that often cause confusion among the parents of children who suffer them.
Measles, chicken pox and rubella are highly contagious viral diseases and, on occasions, difficult to differentiate, especially for parents, since the common element in them are red pimples and stinging in the skin. However, in addition to these grains, there are several key points that differentiate each other.
What is the difference between measles, chicken pox and rubella in children?

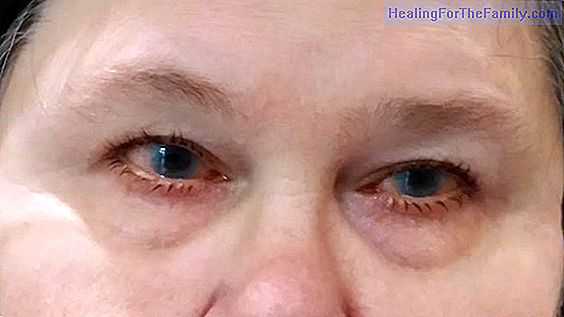
Measles in children
This disease has a high fever, of 39-40º of at least three days, associated with cough, runny nose and red eyes (conjunctivitis). From the point of view of the "grains", what differentiates measles, rubella and chicken pox is that they affect the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet, and do not bleach when we squeeze the skin that surrounds them.
They do not generate itching. If we look at the mouths of these children, we can see some white spots, called Koplik spots. A small percentage of patients develop pneumonia as a complication. Rarely, complications appear in the central nervous system. Its best treatment is preventive, through regulated vaccination.
Rubella in children
In rubella, the fever is not as high as in measles. Nonspecific symptoms may appear, typical of a flu-like condition (scarce catarrhal symptoms, muscle pain), and enlargement of the lymph nodes present behind the ears, in the neck and occipital region.
In this disease, the spots on the skin are pink, can cause itching, and typically begin on the face; As the days go by, they are also visualized in the thorax, abdomen and lower limbs. Complications are infrequent, highlighting neurological complications, platelet descent and arthritis. It can also be prevented, through the use of the vaccine. To emphasize the importance of preventing the appearance of congenital rubella (which appears in unvaccinated pregnant women of this entity).
Chickenpox in children
There is usually no high fever in chickenpox. Characteristically, skin lesions are very itchy in chickenpox. These are usually found in different phases (spots, pimples, vesicles, pustules and scabs), and are distributed throughout the body. The most frequent complication is the superinfection by bacteria of the cutaneous lesions.
It can also cause complications in the central nervous system. From the point of view of their treatment, it is important to administer oral antihistamines to control the itching, and thus prevent the child from scratching. There is an antiviral (called acyclovir) that has been shown to be effective if it is administered in the early stages of the disease. There is also a specific vaccine.