Corion biopsy. What it is used for in pregnancy
Within all the tests that a pregnant woman can undergo during the nine months of pregnancy, we have some that aim to rule out chromosomal abnormalities in the future baby. The best known, because of its frequency, is amniocentesis; however there are others that allow us to see possible congenital de
Within all the tests that a pregnant woman can undergo during the nine months of pregnancy, we have some that aim to rule out chromosomal abnormalities in the future baby.
The best known, because of its frequency, is amniocentesis; however there are others that allow us to see possible congenital defects (the same as with amniocentesis) but that can be detected at early stages of pregnancy. One of them is the chorionic biopsy.
What is the corial biopsy and how is it done in the pregnant woman?
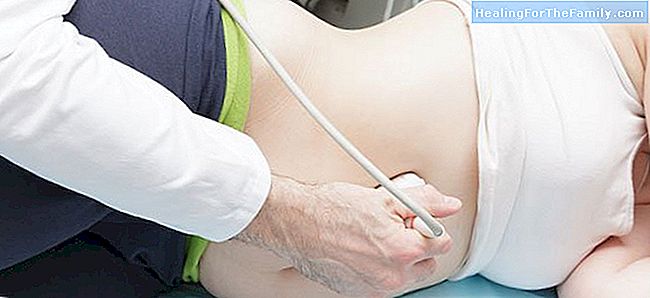
The chorion biopsy consists in obtaining a sample of the chorionic villi (cells that protrude from the placenta in the form of very small fingers); that is to say remains of fetal cells that are housed in the placenta. It is usually done between weeks 10 and 14 of pregnancy.
The most frequent is that the sample is taken through the cervix, through continuous ultrasound monitoring: a semi-rigid forceps is introduced through the vagina, and a sample of the leafy chorion (placenta) is obtained. You can also perform an aspiration of the villi.
The procedure can be a bit painful, but it is fast: it is usually a half hour, from the beginning to the end, and the extraction itself, only lasts a few minutes. Women who have had a chorion biopsy say they feel something similar to when they have a cytology: it may not hurt or feel like a puncture or menstrual pain.
Sometimes, at least, the placenta is accessed through the abdomen, by laparoscopy and under continuous ultrasound monitoring.
When to perform a chorion biopsy on the pregnant woman
This test is indicated when the baby is likely to have congenital anomalies, it is usually recommended to couples with family histories with antecedents or risks for a certain disorder. The samples collected during the extraction are cultivated immediately and the results are obtained within the first 48h, which is considered very fast. What precautions should I have ?:
- I rest 24-48 hours after the puncture.
- Do not make efforts for a while afterwards.
- Administration of anti-D gamma-globulin to all pregnant Rh negative.
Risks of the chorion biopsy for the pregnant woman and the baby
The test has a risk of abortion of seven or eight percent. It can happen that the pregnant woman experiences a sensation of pain or discomfort and a small amount of blood in the following 48 hours.
There are also studies that indicate that a chorion biopsy done before week 11 of pregnancy can lead to defects in the baby's extremities, such as lack of fingers or toes.