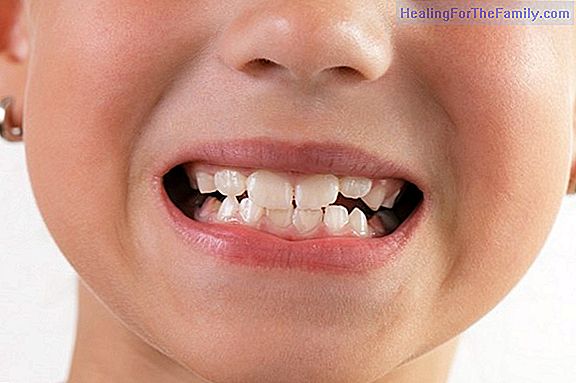
What are the worms and how do they get the children?
The pinworms are intestinal parasites very frequent in the pediatric age. They are white, mobile worms found in the intestines of some children. The female of the parasite moves to the perianal area, especially at night, where it deposits its eggs, which remain attached to the skin or clothes. With
The pinworms are intestinal parasites very frequent in the pediatric age. They are white, mobile worms found in the intestines of some children. The female of the parasite moves to the perianal area, especially at night, where it deposits its eggs, which remain attached to the skin or clothes.
With the scraping of the area, the eggs are placed under the children's nails and if they put their hands to their mouths they can eat them and self-infection is perpetuated. It is common in children who attend day care centers and it is also frequent that several people of the same family have oxiuriasis.
Symptoms of worms in children
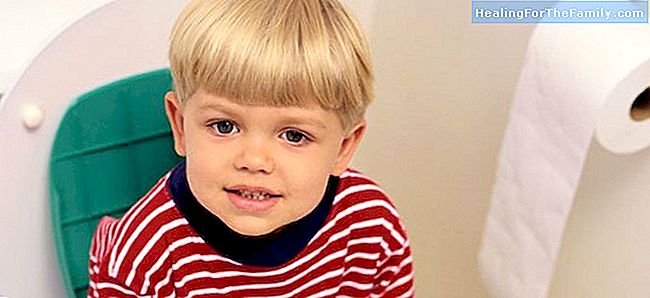
The parasite is called Enterobius vermicularis or pinworms, although in colloquial language we often call these parasites 'earthworms'. The eggs are sticky and can contaminate bedrooms and bathrooms, objects, water and swimming pools. They can pass from one child to another through their hands or sharing toys, clothes or any object, so it is a fairly common infection, and the symptoms are not serious, but they are annoying.
These are the worm symptoms in children:
- They tend to provoke, especially at night, itching in the anal region, foreign body sensation or genital irritation especially in girls. El - Sleep is often uneasy or with night terrors, nightmares or frequent awakenings.
- Scratch wounds can be seen, even with superinfection or inflammation.
Diagnosis and treatment of earthworms in childhood
The
Graham test is performed by placing transparent adhesive paper in the early morning in the perianal region, to visualize under the microscope the eggs deposited by the female in the perianal area. Adult worms can also be directly visualized in the perianal or genital region. The child should be treated and if possible also the siblings and family.
A medication (mebendazole, single dose) is administered and repeated after 15 days, since the medication eliminates the worm, but not the egg, and the dose must be repeated to eradicate the worms that have developed in that period. This second dose is very important, we must not forget to administer it to children. Hands and nails, and toilets should be washed thoroughly. Eggs can remain on the clothes for a long time, so they must wash with hot water and bleach the bedding, pajamas and towels.
The shower or bath in the morning is highly recommended since it eliminates a large proportion of the eggs.